Adenoids are an essential part of the human immune system, playing a critical role in defending against infections, particularly in childhood. However, issues with adenoids can lead to a variety of health concerns, including respiratory problems, frequent ear infections, and sleep disturbances.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about adenoid, their function, common problems, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Are Adenoids?
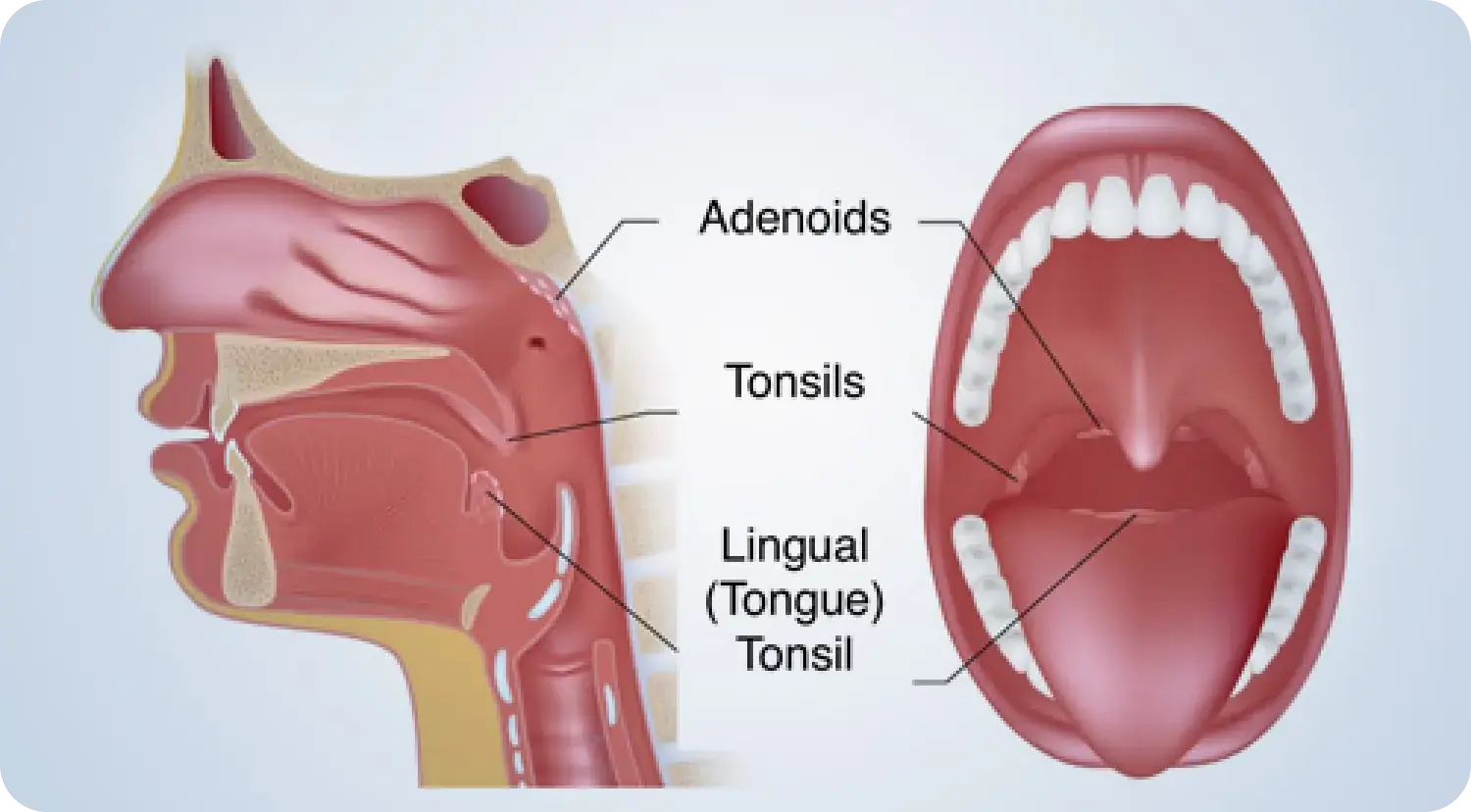
Adenoids are small masses of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the nasal cavity, just above the roof of the mouth. They are part of the lymphatic system and help the body fight infections by trapping pathogens that enter through the mouth and nose. Although they are similar in function to tonsils, which are located at the back of the throat, adenoids are not visible in the mouth, as they are deeper in the throat.
Adenoids are more active during childhood and typically shrink as a person matures. In some cases, however, the adenoids can become enlarged, leading to a variety of health issues.
How Adenoids Function in the Immune System
Adenoids work alongside other lymphatic tissues, like the tonsils, to prevent infections. When harmful bacteria or viruses enter the body through the mouth or nose, the adenoids trap these invaders and help produce antibodies to fight them. This process is especially crucial in children, as their immune systems are still developing.
However, the adenoids themselves can sometimes become a source of health problems. Enlarged adenoids, for example, can block the airway, leading to breathing difficulties, snoring, or sleep apnea. Additionally, adenoid infections can cause ear problems, including fluid buildup, and may contribute to sinus infections.
Common Problems Associated with Adenoids
While adenoids are beneficial for immune defense, several issues can arise, especially when the adenoids become enlarged. Below are the most common problems linked to the adenoids:
1. Enlarged Adenoids
Enlarged adenoids are a common problem, especially in young children. As the adenoids grow, they can obstruct the airway, making it difficult to breathe through the nose. This condition may lead to a range of symptoms:
-
Mouth breathing: Children with enlarged adenoids may resort to breathing through their mouths because their nasal passages are blocked.
-
Snoring: Blocked airways can lead to loud snoring, especially during sleep.
-
Sleep apnea: In more severe cases, enlarged adenoids can cause obstructive sleep apnea, a condition where breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep.
Enlarged adenoids can also contribute to recurrent ear infections due to the blockage of the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the throat. This can lead to fluid buildup in the ears, affecting hearing and causing discomfort.
2. Adenoiditis
Adenoiditis is an infection or inflammation of the adenoids, often caused by viral or bacterial infections. Symptoms of adenoiditis include:
-
Sore throat and difficulty swallowing
-
Fever and general fatigue
-
Nasal congestion and drainage
-
Ear infections and hearing problems
Adenoiditis is common in children, as their immune systems are still developing. However, it can also affect adults, particularly if they have had previous issues with their adenoids.
3. Chronic Infections
When adenoids become chronically inflamed or infected, they may need to be removed. This is typically the case if the infections are frequent or do not respond to antibiotics. Chronic diseases can also lead to long-term complications such as hearing loss or problems with speech development in children.
Symptoms of Adenoid Problems
The symptoms of adenoid problems can vary, but common signs include:
-
Frequent nasal congestion or a runny nose
-
Mouth breathing, especially during sleep
-
Snoring or noisy breathing
-
Difficulty swallowing or a feeling of a lump in the throat
-
Ear infections or fluid in the ears
-
Bad breath
-
Sleep disturbances, such as restless sleep or waking up frequently during the night
-
Speech problems, such as a nasal or “stuffy” voice
How to Diagnose Adenoid Problems
If you suspect that your child or yourself has adenoid problems, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. The diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, during which the doctor will look for signs of nasal obstruction, enlarged tonsils, or signs of infection.
In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be needed, such as:
-
X-rays: A doctor may use an X-ray to determine if the adenoids are enlarged.
-
Endoscopy: This involves inserting a small camera through the nose to look directly at the adenoids and the surrounding tissues.
-
Hearing tests: If ear infections are frequent, hearing tests may be conducted to check for fluid buildup in the middle ear.
Treatment Options for Adenoid Problems
The treatment for adenoid issues depends on the severity of the problem. Below are the most common treatment approaches.
1. Conservative Treatments
For mild symptoms or slightly enlarged adenoids, conservative treatments may be enough. These can include:
-
Saline nasal sprays or irrigation to relieve nasal congestion
-
Decongestants to reduce swelling and open nasal passages
-
Antibiotics are used if a bacterial infection is present
-
Steroid nasal sprays to reduce inflammation
In most cases, these treatments can alleviate symptoms without the need for surgery. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, more aggressive interventions may be required.
2. Surgical Removal (Adenoidectomy)
In cases of chronic adenoiditis or significant breathing problems, surgery may be recommended. An adenoidectomy is a procedure to remove the adenoids. It’s a relatively simple and safe surgery, performed under general anesthesia.
After surgery, most patients experience a significant improvement in symptoms. The procedure is usually performed on children, but it can also be beneficial for adults who experience severe issues with their adenoids.
Risks of Surgery include bleeding, infection, and the possibility of regrowth in rare cases. However, complications are minimal, and the procedure generally has a high success rate.
Prevention of Adenoid Problems
While it’s not always possible to prevent issues with the adenoids, there are a few strategies that may reduce the risk of complications:
-
Practice good hygiene: Frequent hand washing can help reduce the spread of infections.
-
Avoid secondhand smoke: Exposure to smoke can irritate the adenoids and increase the risk of infections.
-
Healthy diet and exercise: Keeping the immune system strong through proper nutrition and regular physical activity can help prevent infections.
People Also Search: Baddiehubpro
Conclusion
Adenoids are an important part of the immune system, particularly in childhood, but they can also lead to health problems if they become enlarged or infected. Symptoms like nasal congestion, mouth breathing, snoring, and frequent ear infections can indicate an issue with the adenoids. Treatment options range from medications to surgical removal, depending on the severity of the condition. If you or your child experiences persistent symptoms related to adenoids, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for an appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs
1. Can adenoids grow back after removal?
In rare cases, adenoids may regrow after surgery, especially if the tissue is not entirely removed. However, this is uncommon, and most people experience long-term relief after an adenoidectomy.
2. Are there any risks associated with enlarged adenoids?
Yes, enlarged adenoids can cause breathing difficulties, sleep apnea, ear infections, and speech problems. If left untreated, they can lead to long-term complications like hearing loss or speech delays.
3. Can enlarged adenoids affect a child’s growth or development?
In severe cases, enlarged adenoids can contribute to poor sleep quality, which may impact a child’s overall health, behavior, and development. This is why it’s essential to address the problem early on.
4. Can adults have problems with their adenoids?
While adenoid issues are more common in children, adults can also experience problems, particularly if they have a history of chronic infections or nasal obstructions.
5. How do you know if a child needs an adenoidectomy?
Your healthcare provider will assess the severity of the symptoms and may recommend surgery if the child experiences chronic infections, breathing problems, or sleep apnea that do not improve with other treatments.